

Clemson University Life Sciences Facility
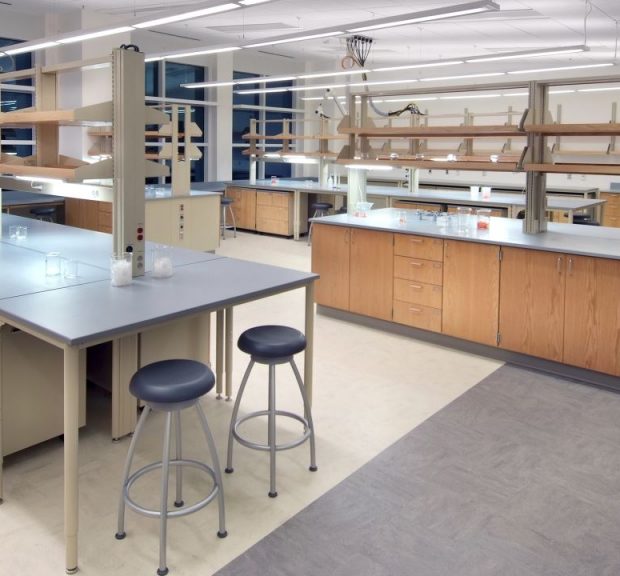
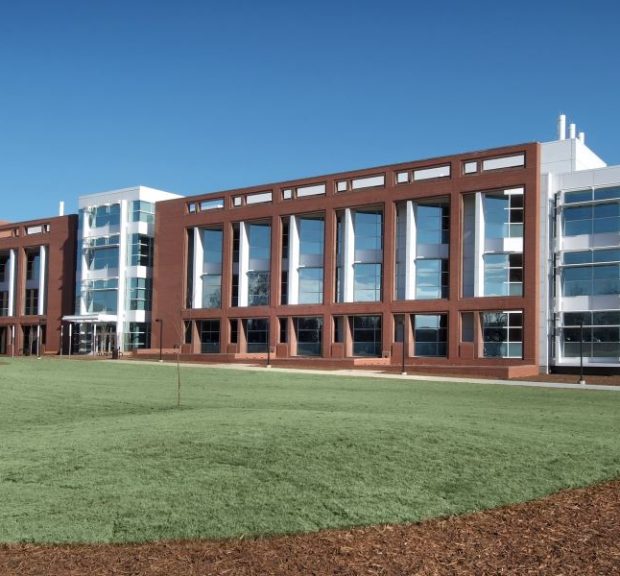
The Life Sciences Facility is a flexible laboratory, teaching, and faculty office environment, and is the first phase of a Life Sciences Quadrangle on the Clemson campus. The building supports the College of Agriculture, Forestry and Life Sciences. The teaching space includes three microbiology teaching laboratories, including support for upper-level undergraduate and graduate level classes. The building accommodates twenty-three principal investigators and their students, along with technical and service support staff. The common thread of research emphasis is on microbiology, biochemistry, food safety and genetics. Sustainable features include chilled beams, condensing boilers, and daylight harvesting.
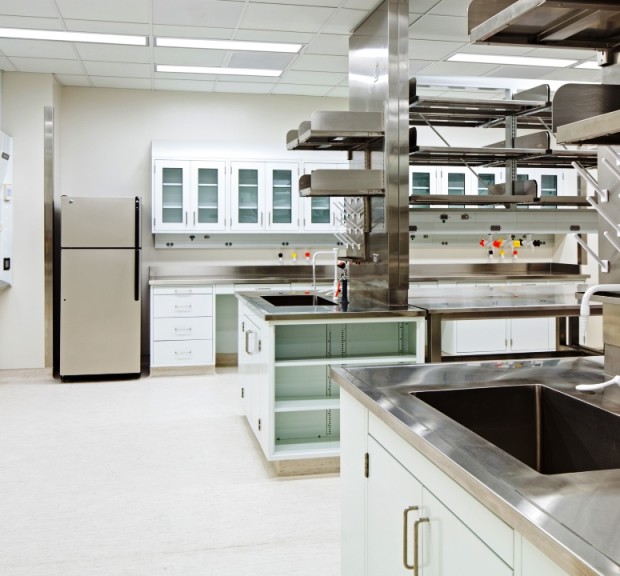
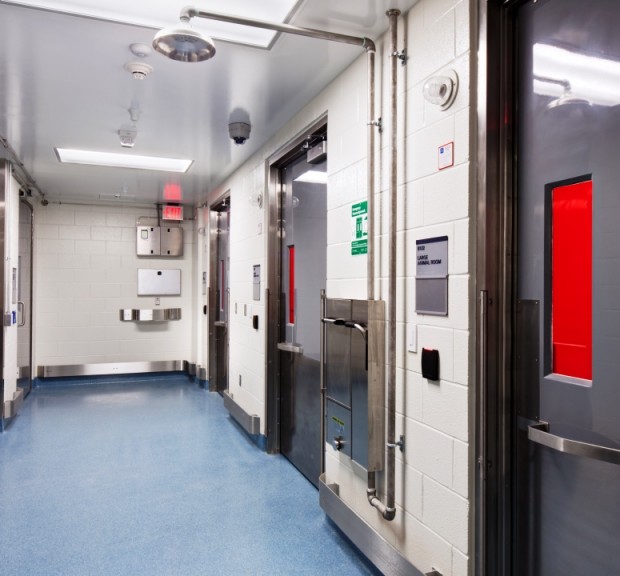




University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Marsico Hall
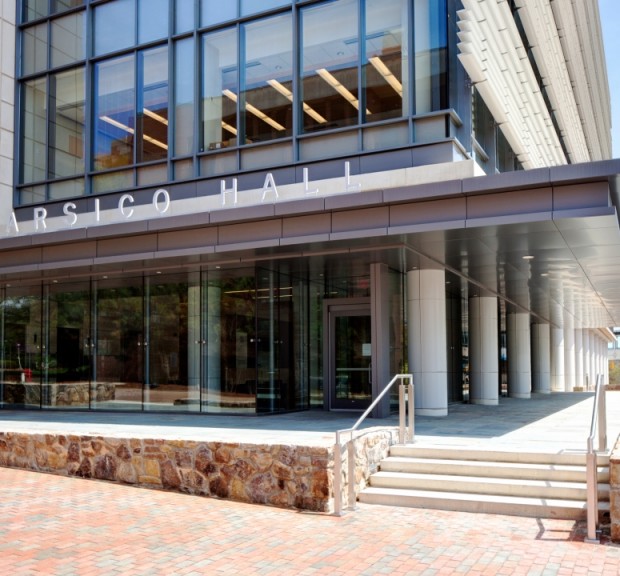
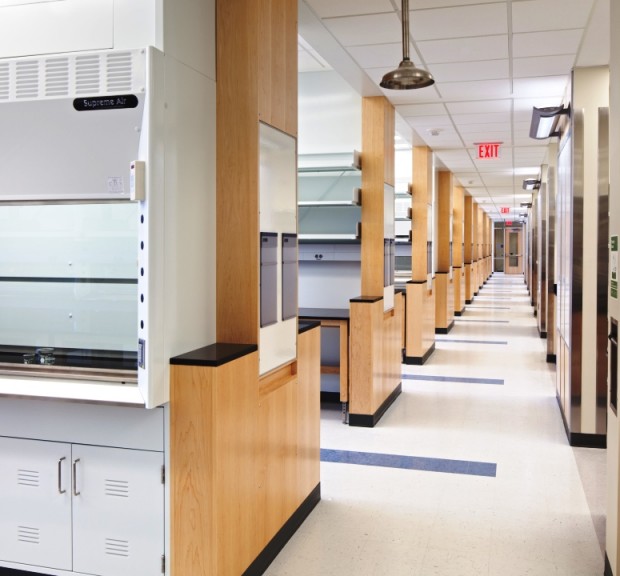
Marsico Hall is a high-rise research facility including laboratories for drug discovery and delivery, a vivarium housing 3,000 small and 18 large animal cages, general wet laboratories, and a campus district energy plant. Marsico Hall houses many of the School of Medicine’s and the Eshelman School of Pharmacy’s research programs, including the Marsico Lung Institute, the Biomedical Research Imaging Center, and researchers from the Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, nanomedicine, microbiology and immunology, and pharmaco-engineering. Underground chilled water piping work includes the replacement of 800 linear feet of 24″ chilled water mains and a new 18″ connection to the Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center. Imaging equipment located in the facility includes a cyclotron, a small bore 9T MRI, a 3T MRI, MR/PET, PET/CT, and multiple NMRs. Sustainable features include a district energy plant with heat recovery chillers, a runaround loop energy recovery system, variable volume laboratory controls, a non-potable water system, low flow plumbing fixtures, and laboratory equipment water saving options. This building is pursuing LEED Silver certification.
Acoustics
Mechanical and electrical systems noise and vibration control.
Audio-Visual
Audio-visual systems including videoconferencing and distance learning technologies for numerous medium and small classrooms and conference rooms.
Campus Infrastructure
Extension of the campus steam system, including the addition of manholes and precast pipe tunnels.
Communications
Voice and data pathways and cabling systems, complete wireless LAN coverage, and a raceway system supporting a distributed antenna system (DAS) for connection to future campus in-building wireless systems.
Security
Video surveillance, access control, and alarm monitoring systems monitor laboratories and audit/log users into controlled spaces.
Plumbing
Two pure water generating systems are provided for the building, each serving three floors. Each system is sub-divided into a low-grade system that generates RO-quality water for distribution to glassware washers and clean steam generators for sterilizers and into a high-grade system (supplied from the low-grade system) that generates deionized water for distribution to laboratory pure water faucets. Each low-grade sub-system is capable of producing a minimum of 1,080 gallons per day; each high-grade sub-system is capable of producing a minimum of 675 gallons per day. The typical low-grade sub-system consists of pre-filters, a water softener, carbon filters, reverse-osmosis unit, master control unit (to control both the low- and high-grade sub-systems), storage tank, distribution pumps, ultraviolet sterilizer, post-filter, and distribution piping. The typical high-grade sub-system consists of a storage tank, distribution pumps, ultraviolet sterilizers, deionization vessels, post-filter, water quality monitor, and distribution piping.
Electrical
Electrical design includes landscape and site lighting for a quad between Marsico Hall and the Genetic Medicine Building.
Awards
Marsico Hall is the recipient of the 2014 National ENR Excellence in Safety Award and the 2014 ENR Southeast Award of Merit in the Higher Education/ Research category.
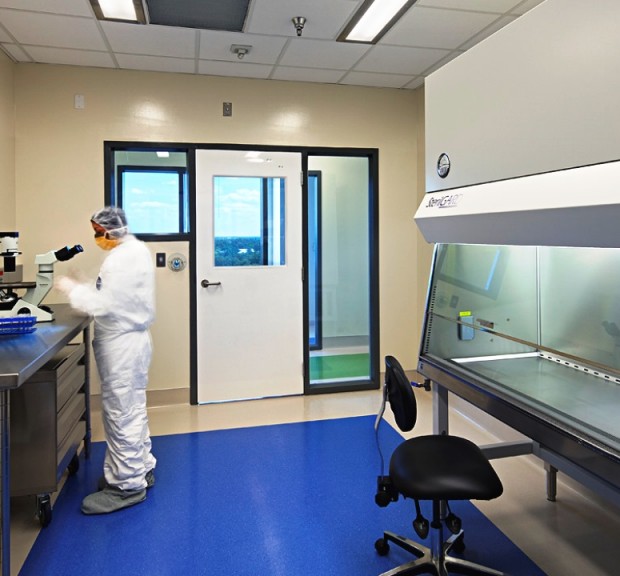
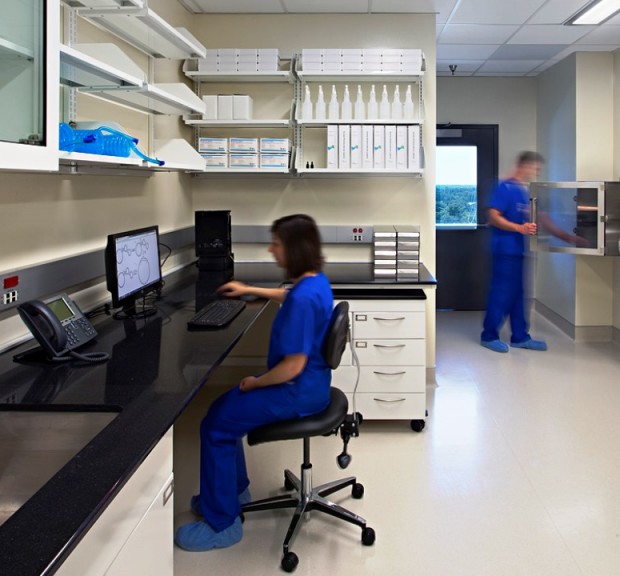
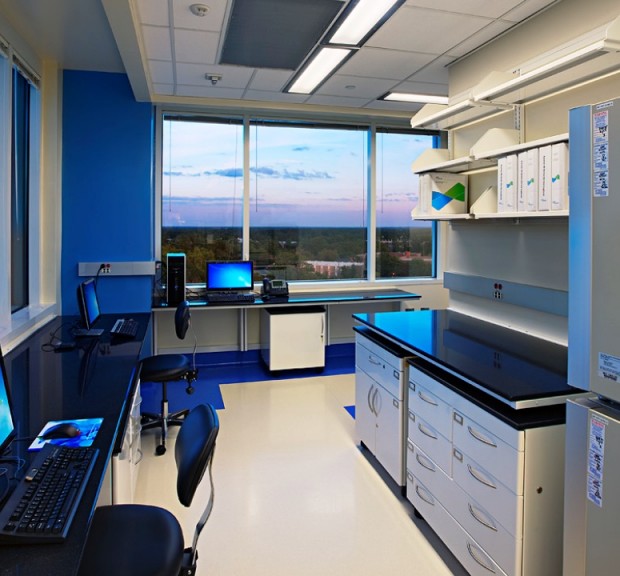



Duke Health The Robertson Clinical & Translational Cell Therapy Program
Addition of three ISO 7 cleanrooms on the Ninth Floor of the North Pavilion for the Duke Translational Research Institute Group.

Georgia Public Health Laboratory
This replacement regional BSL-3+ laboratory facility functions as a back-up to facilities located in Albany and Decatur, Georgia, as well as performs the workload of the previous regional laboratory. The building houses four separate laboratory suites with different functions: CT (Chemical Terrorism) Suite, BT (Biological Terrorism) Suite, Training and Production Laboratories, and Surge Laboratories. All exhaust from the laboratories is HEPA filtered and each laboratory suite has its own dedicated HEPA filter bank. The entire facility is served by emergency power and redundancy is provided for all major mechanical equipment. The effluent waste from the laboratories passes through an effluent decontamination system. The laboratory waste piping is double-wall for secondary containment, and the piping in the BT Suite is provided with leak detection. The facility includes several provisions to prevent a terrorist attack on, or tampering with, the building or building systems, laboratory production space, a mail screening area, an “unknowns” room for examination of potentially hazardous deliveries, a training classroom, a training laboratory, offices, and conference room space.
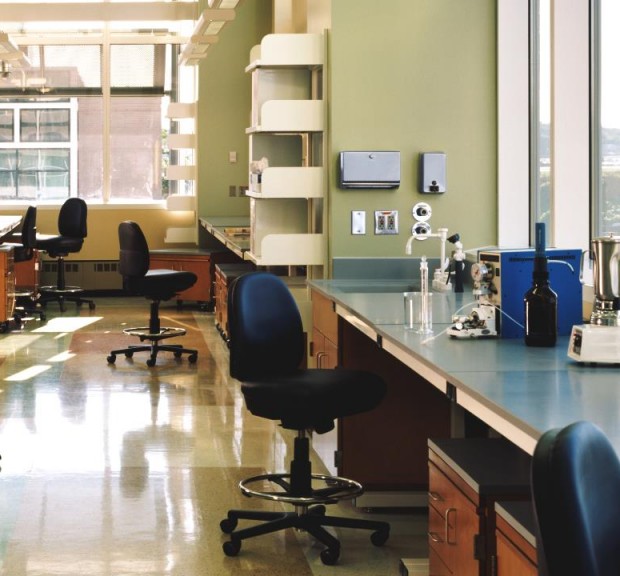
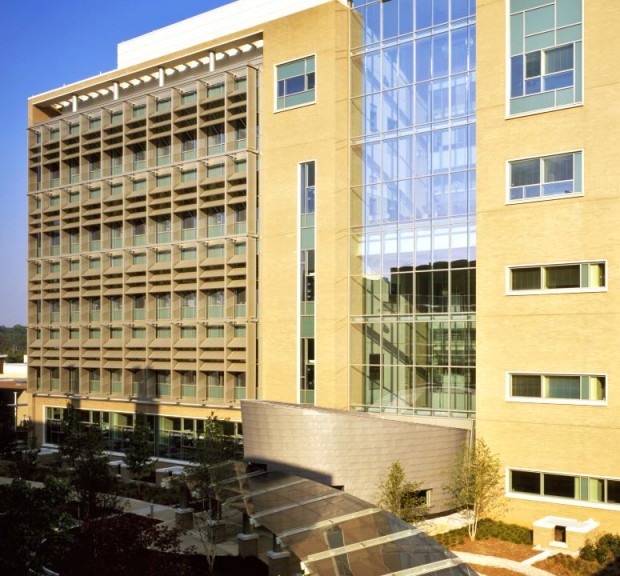


CDC National Center for Environmental Health
Housing the Division of Laboratory Sciences for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Center for Environmental Health includes a combination of laboratory, laboratory support, and scientific personnel office space to support the Division’s programs.
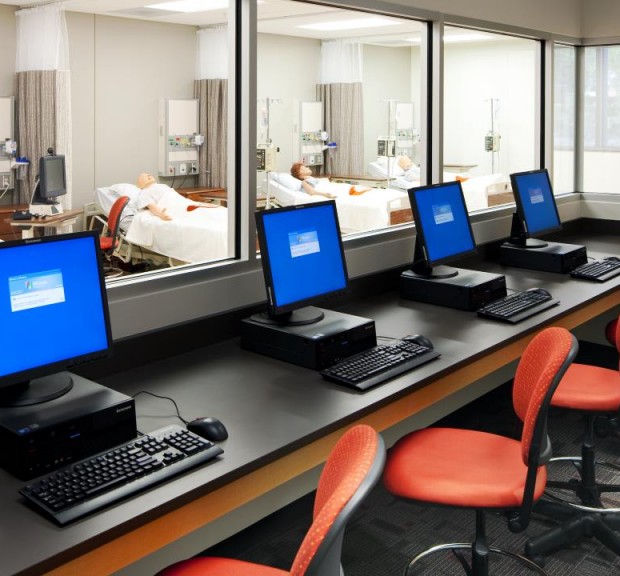


Columbus Technical College Dr. Robert L. Wright Jr. Health Sciences Center
The Dr. Robert L. Wright Jr. Health Sciences Center provides occupational education and training programs to satisfy the increasing demand for health care workers in the Columbus area. The facility houses existing health care programs including Allied Health Assistant, Dental Hygiene, Dental Assisting, Nursing, Practical Nursing, Radiologic Technology, Patient Care Assisting, Phlebotomy, Surgical and Pharmacy Technology, Paramedic and EMT, and Medical Assisting. New health care programs housed in the building include Medical Office Management, Health Information Technology, Respiratory Care Therapy, Diagnostic Medical Sonography, and Medical Coding.
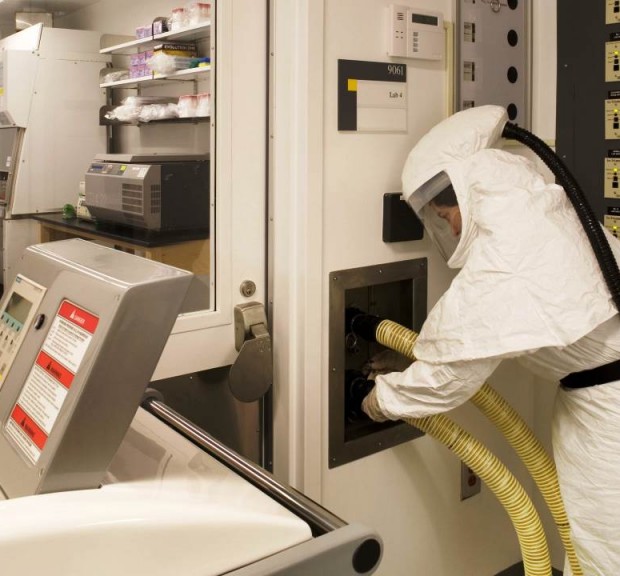
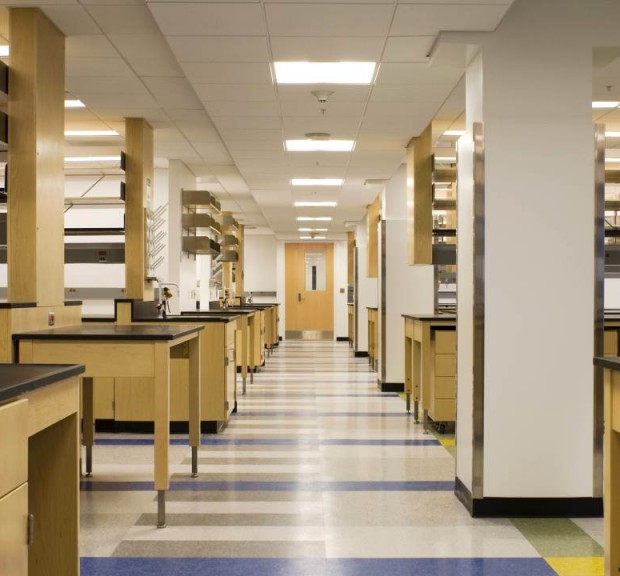



University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Burnett-Womack Clinical Research Building
Renovation of the nine story Burnett-Womack Clinical Research Building comprising both laboratory and office space. The building includes a clinical trials and training facility containing imaging and diagnostic equipment and a BSL-3 laboratory suite. Improvements in the building include an upgrade to current laboratory planning standards, replacement of outdated engineering systems, upgrades for code requirements including fire and life safety and ADA compliance, integration of flexible systems for casework and utility distribution, and improvements to all laboratories and offices including the replacement of casework and equipment.
This is the recipient of an Eagle award for Excellence in Construction from the Associated Builders and Contractors Carolinas Chapter, 2007.
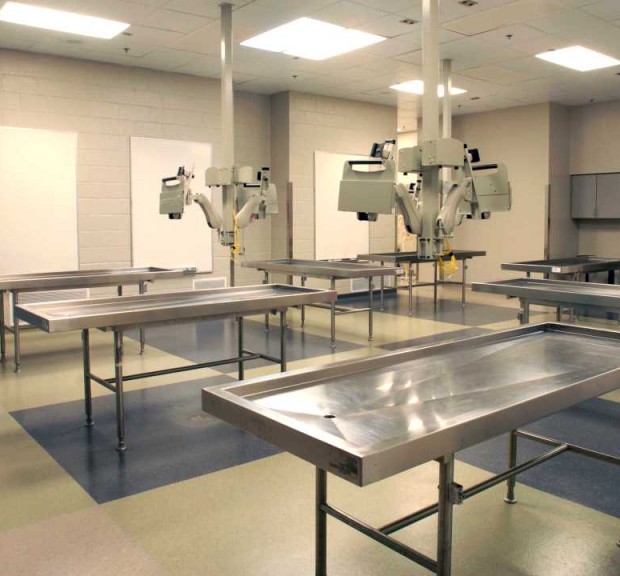
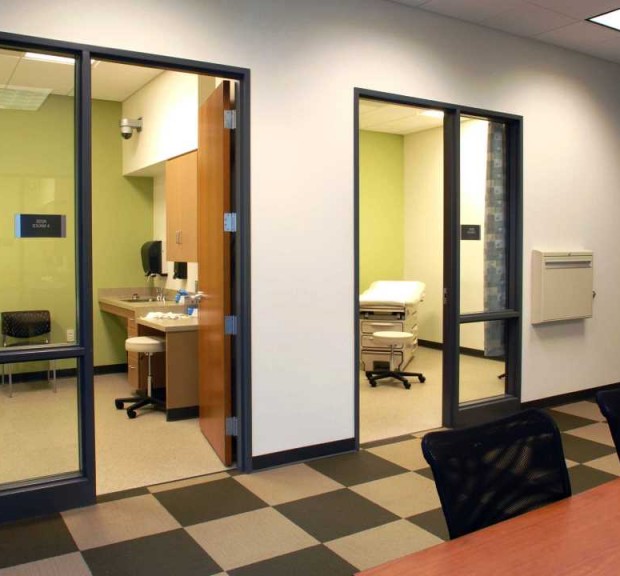



Emory University James B. Williams Medical Education Building
A 56,000 square foot renovation of, and 101,000 square foot major addition to, the Anatomy and Physiology Buildings to create the James B. Williams Medical Education Building. The building includes a 200 seat auditorium, large classrooms, administrative areas, an atrium, a morgue, and grossing and anatomy laboratories for teaching. Sustainable features include under floor air distribution, energy efficient lighting and controls, and creative use of air to reduce outside air heating and cooling loads.
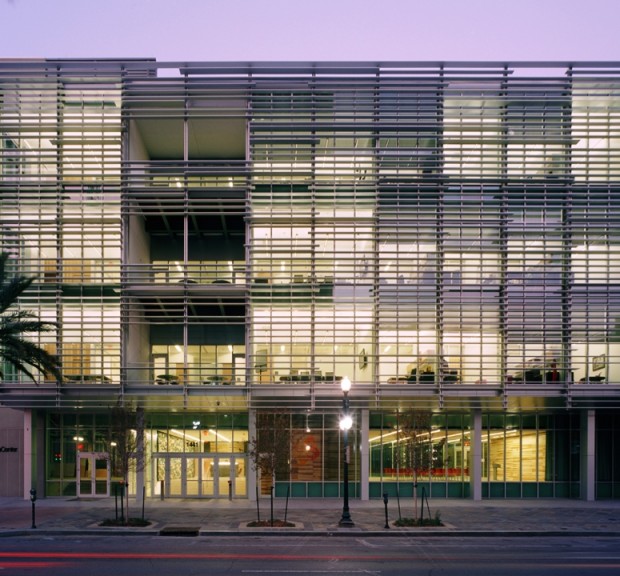
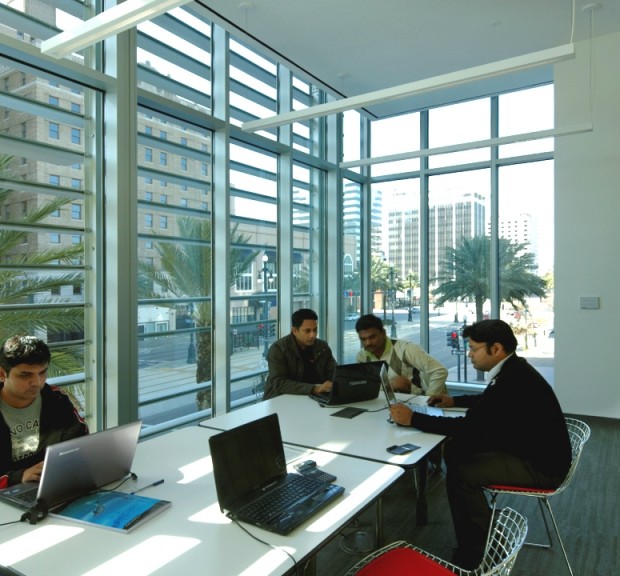



New Orleans BioInnovation Center
Offering support and guidance to emerging biotechnology companies commercializing technologies primarily derived from New Orleans-based universities, the New Orleans BioInnovation Center provides tenants with wet laboratories, office space, and meeting and conference spaces; and caters to a wide variety of companies, ranging from pre-startups and start-ups to maturing and expanding businesses. Laboratory spaces range from bench space for individual efforts to full laboratory suites. Each laboratory is environmentally isolated with fume hoods, emergency backup systems, administrative space, dedicated phone and data lines, and access to shared equipment. Construction documents were also provided for an 11,000 square foot FDA compliant clinical manufacturing facility, including ISO 6, 7 and 8 cleanrooms. Sustainable features include utility monitoring systems, demand controlled ventilation, variable volume laboratory airflow controls, daylighting, lighting controls, bilevel lighting, and high efficiency transformers.
Intelligent building systems deployment includes an integrated building management system normalizing data from building automation, facility metering and lighting control systems. Deployment also consists of automated analytics, fault detection, and diagnostics platform.
The New Orleans BioInnovation Center received a 2013 American Architecture Award from The Chicago Athenaeum: Museum of Architecture and Design and The European Centre for Architecture Art Design and Urban Studies.
NOBIC was also selected as one of the 2015 COTE Top Ten Green Projects by the American Institute of Architects (AIA) and its Committee on the Environment (COTE).
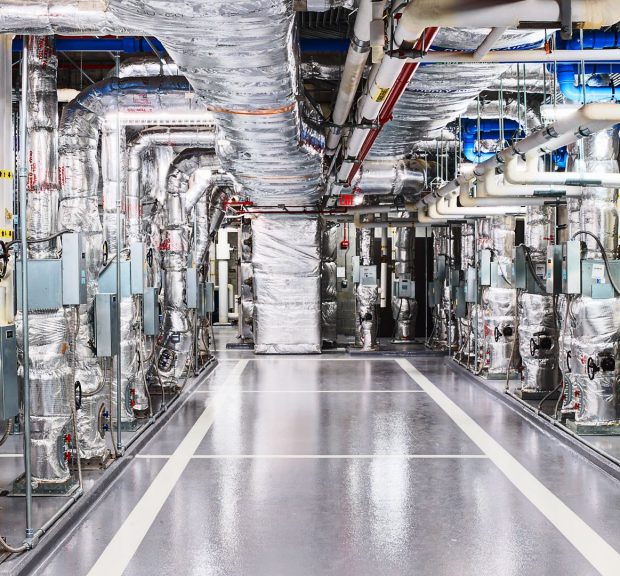

Yerkes National Primate Research Center Dual-Function Facility
The three story Dual Function Facility includes the Emory Institute for Drug Discovery and the Center for Innovative Genetics. Researchers in the facility specialize in addressing previously unmet needs regarding infectious diseases and issues relating to transplant surgeries. The facility houses animal research facilities including ABSL-3 animal holding rooms, animal treatment and housing rooms, transplant operating rooms, laboratories, interstitial space for mechanical and electrical equipment and distribution, a tissue digester and a necropsy room. The facility has a dedicated boiler and chiller plant and is designed to NIH DRM standards. The building has N+1 redundancy for air handling equipment for backup in case of an equipment failure, which also provides energy savings during normal operation.
